Why set up an offshore captive insurance company? Tax benefits and savings on insurance premiums are two of the many reasons that attract so many businesspeople to set up such a captive insurance company. For example, research shows that about 80% of the Standard and Poor 500 (S&P 500) companies own one or more captive insurance companies. Offshore captive insurance is the main source of insurance for both large and small companies. U.S. Internal Revenue Code Section 831(b) specifically allows for this particular type of insurance company. The shareholders or principles of the insured company also own the insurance company. The insured, related company which pays the premiums into the plan receives a tax deduction for the premiums as an ordinary and necessary business expense.
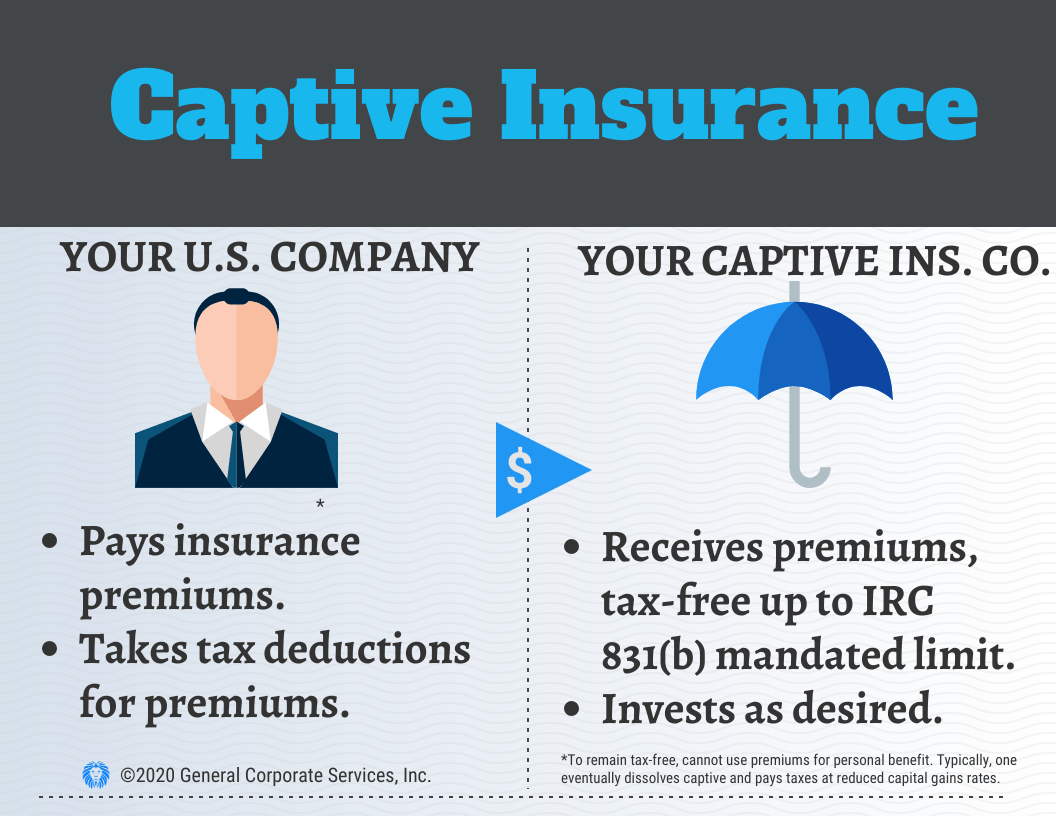
How Does an Offshore Captive Insurance Company Work?
The insured companies (or individuals) pay the insurance premiums. The funds are deposited into an account in the name of the captive insurance company. The people who own the insurance company typically own own the insured company or companies as well. So rather than an outside insurance company profiting from the premiums and claims, those who established the entity can benefit from the profit that institutional insurer would normally realize.
Captive Insurance Company Tax Benefits
The company paying the premiums receives a tax deduction, and the captive insurance company receiving the premiums receives the first $2.35 million tax-free (as of 2020). The statutory captive insurance company will elect to be classified as a domestic insurance company as indicated under IRC Section 953(d). It will, therefore, file US tax returns annually. However, premium income up to the first $2.35 million is exempt from taxation. In the following calendar year, another $2.35 million can be contributed, for a total of $4.7 million over two years, $7.05 million in premiums are tax deductible over three years, etc.
Offshore Captive Insurance Definition
A captive insurance company is an insurance company that the companies it insures typically own and control. So, its main purpose is to insure the risk of its owners while allowing them to benefit from the underwriting profits. Laymen may refer to the arrangement as self-insuring, alternative risk transfer or alternative insurance.
Offshore Captive Pros and Cons
Financial havens with strong insurance statutes are the locations where professionals form the most companies. In addition to the tax benefits described above there are several additional convincing reasons why captive offshore insuring vehicle should be considered. One is able to “self insure” to an extent not available otherwise. The cost of insurance are often significantly reduced. Plus, the arrangement can enhance your risk management. Moreover, if a standard policy is not available or extraordinarily expensive, the plan may be the only viable option. Professional malpractice, pollution and hazardous materials as well as catastrophic risk are excellent examples of rates-gone-awry. US insuring companies frequently raise rates or deny coverage without warning. Whereas, owning your own offshore captive company can give your plan longstanding solidity and direct access to reinsurance markets.
Whereas an offshore captive insurance company can offer significant savings on insurance premiums and significant tax benefits, one contrary point is that they are not inexpensive to establish or operate. There is the initial setup fee, the captive insurance manager and the annual renewal costs. The costs vary from place to place so it is best to use the number of form that is located here in order to obtain additional information. The key is to make sure that the income that the insured party generates is sufficient. That is, you want to make sure that the money saved in taxes and premiums far offset the initial and annual costs.
Domestic vs. Offshore Captive Insurance
There are some US states and at least one Canadian province with statutes on the books that enable domestic captives. However, there are particularly attractive benefits to going offshore. These include significantly lower costs, possible tax benefits and fewer regulations.
Investing Premiums
The money inside the insurance company is, in turn, invested. One popular and stable choice is to invest the money with a Swiss bank account that has a money management division. Thus, the premiums are deductible and the company receives premiums tax-free. Naturally, the captive insurance company pays annual taxes on the income that the investments generate.
Types of Captive Insurance Companies
A captive is a wholly owned subsidiary of a company that is not primarily in the insurance industry. Its main function is to insure some or all of the risk of its parent company. As the industry has grown those involved have sought new methods of enhancing the captive structure to create means by which a variety of industries can benefit. Here are a number of different structures that businesspeople use.
- Single Parent Captives – Only underwrite the risk of related group companies.
- Diversified Captives – Underwrite unrelated risk in addition to related group companies.
- Association Captives – Underwrite the risk of members of a specific industry-type or trade-association. Medical malpractice is often insured in this fashion.
- Rent-A-Captives – Companies that offer access to captive structures without needing to establish one’s own insurance company. The participant pays for the use of the company and needs to provide collateral so that the rent-a-captive is not exposed to substantial risk experienced by the participant.
- Special Purpose Vehicles (SPV’s) – Used to secure risk. These are reinsurance companies that execute contracts with their parent company and yield the risk to risk the capital markets. This is typically accomplished by a bond issue.
- Agency Captives – Established by insurance agents or brokers to enable them to participate only in low-risk activities under their control.
Captive Insurance Requirements
To comply with IRS requirements, the captive insurance company premiums need to exceed investment income. Additionally, the policies that the captive issues need to comply with the “risk distribution” and “risk shifting” requirements. In order to comply, the company can obtain reinsurance. This is done in the international reinsurance markets whereby “pooling” arrangements are utilized. This can successfully minimize the costs and the help to protect against to claims by unrelated companies. The finer points and investment required to establish the structures depend on the needs and desired outcomes.
Accounting
Because this technique is common among many well-known companies, there are a number of highly regarded accounting firms that deal with the necessary tax and reporting duties for statutory captives.
Is it a Listed Transaction?
The IRS has issued Notice 2004-65 which has successfully de-listed the Section 831(b) statutory captive insurance company as a tax shelter. So, it is not a listed transaction and the IRS does not require special notification that one is participating in such a program. IRS Commissioner Mark. W. Everson has states, “Based on disclosures from taxpayers and examination of tax returns, we have determined problems associated with these transactions are no as prevalent as initially believed. Accordingly we are no longer classifying them as listed transactions.”
See Captive Insurance Minimum Capital and Surplus Requirements by jurisdiction.
For More Information
Offshore captive insurance offers some significant benefits to many companies, including small to large Fortune 500 firms. To form a captive insurance company, please feel free use the number or form on this page.
This purpose of this page is to give a general overview of the subject matter. It involves complex legal and tax planning knowledge. We do not intend to give nor should you consider it tax or legal advice. We highly recommend keeping licensed tax and legal counsel throughout its operation and use.
Would You Like More Information?
If you would like more information about forming your own captive insurance company, please feel free to call the number above. Alternatively, you can complete the free consultation form on this page. You can speak with one of our staff attorneys to discuss your needs.